‘ACCELERATE‘ by EV2 Ventures is a multi-part article series on the smart mobility landscape in India. In the fourth edition, we outline our perspective on the collective efforts that need to assimilate in the mobility space to achieve India’s target of Net zero Emissions by 2070.
The Growth of Power Generation in India: Generation, Transmission & Distribution
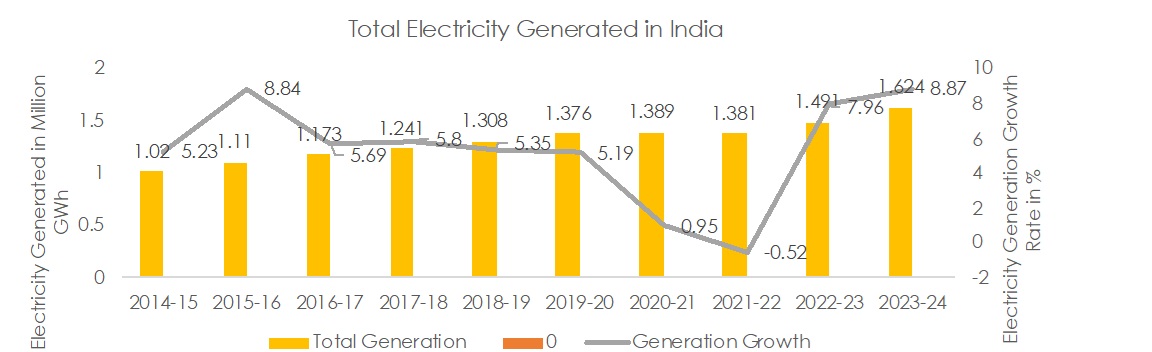
After, China & USA, India sits as the world’s third-largest electricity producer, boasting a total installed capacity of 417 GW as of May 2023. The ambitious target for 2023-24 is 1.75 million GWh, representing a 7.2% increase from FY 2022-23 where the total electricity generation reached 1.62 million GWh. The CAGR of total installed generation capacity was 7.7% during the period from 2008-09 to 2022-23. The CAGR in RES was 17.4%, whereas it was 5.7% in all other sources during the period.
Government of India has set an ambitious target for enhancement of non-fossil fuel energy capacity to 500 GW (179 GWh presently) by 2030 showing a CAGR of 15%
The transmission sector opened to private investments in 1998, but characterized by high sunk costs, operates as a natural monopoly, limiting entry for non-public entities. Private investments require approval from CERC, although the public sector dominates. The Ministry of Power’s plan aims to integrate over 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, providing visibility and investment opportunities for developers.
Bulk transmission (220 kV & above) grew from 2.21 lakh ckm in 2008-09 to 4.71 lakh ckm in 2022-23, reflecting a 5.6% CAGR. Substation transformation capacity increased from 2.89 lakh MVA to 11.80 lakh MVA, with a CAGR of 10.6% during the same period, as shown below.
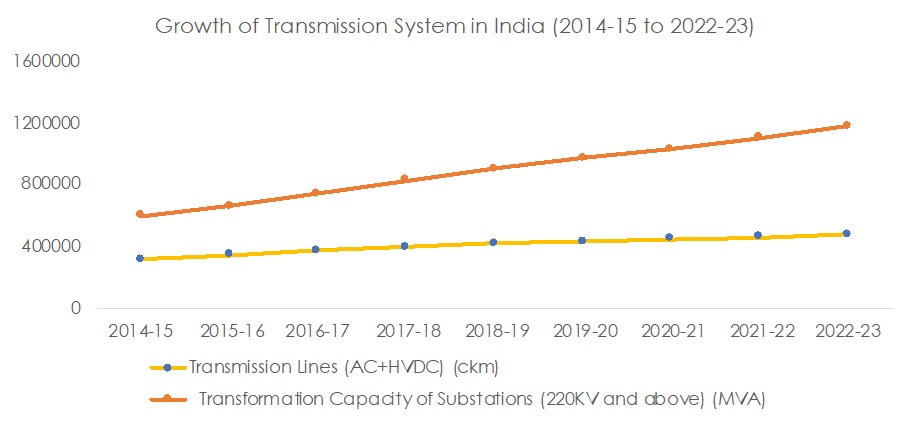
Source: CEA
The distribution sector, a vital component in the electricity supply chain, is predominantly owned by State Electricity Distribution Companies (DISCOMs)/State Electricity Boards (SEBs). As per the latest available ‘Report on Performance of State Power Utilities2021-22’ published by Power Finance Corporation Ltd (PFC), the average all-India AT&C losses were about 16.42% in 2021-22. More than 90% of these losses can be attributed to Transmission and Distribution Losses, which correspond to electricity produced but not paid for. The government is prioritizing grid modernization and smart metering to address distribution challenges.
Consumption
# Projected Generation & Consumption according to historical CAGRs. Export & Import of electricity along with AT& C Losses not included.
The consumption reached 1503.65 BU KWH i.e. 1.5 million GWh in 2022-23, according to the Central Electricity Authority (CEA). This represents a 9.5% increase compared to 2021-22.
Per capita consumption:
In financial year 2022, it was around 1.3 megawatt-hours (MWh) per capita. This value shows the average electricity consumption per person in India (CERC). Despite being the third-largest producer, India’s per capita electricity consumption remains low at 1,327 kWh (FY 2023) as compared to the international average of around 3577 kWh. The residential sector consumes 24% of total electricity, followed by agriculture (18%) and industry (17%) (Source: IEA, 2022).
India has become a net exporter of power, exporting 2,410 GWh to Bangladesh, Nepal and Bhutan in FY23
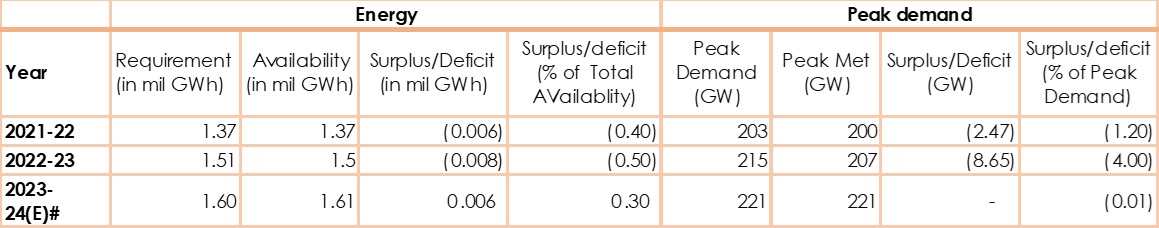
Is the electricity generation enough?
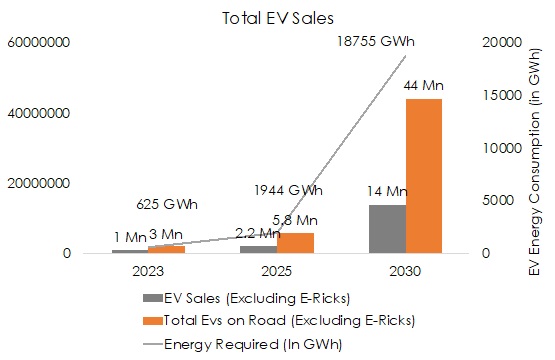
-Electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure and adoption are in their nascent stages. With 3.2 million EVs sold till date with 1.7 Mn 2-Wheelers, 1.2 Mn 3-Wheelers, 150k 4-Wheelers, and 5000 buses, the total energy requirement for 2023 was a mere 625 GWh, amounting to the per capita consumption of less than 1 KWh.
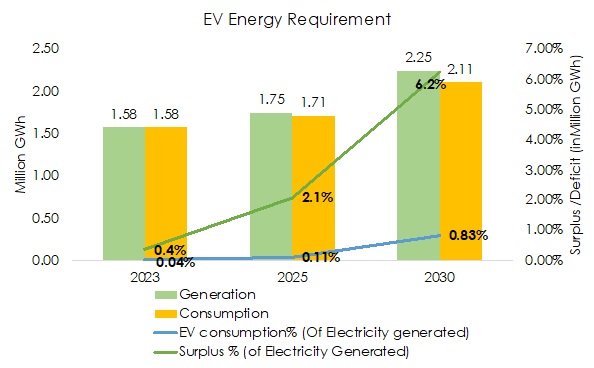
-With the electric vehicle market expected to grow at a CAGR of 44% to roughly 14.5 million EV Sales annually (excluding E-rickshaws) by 2030, the energy requirement of the total EVs on road i.e. around 44 million vehicles would be roughly 19,000 GWh/year** i.e. less than 1% of the total expected energy generation of 2.2 million GWh.
– The electricity requirement of EVs is expected to grow at a CAGR of 63% but due to such low quantum, the energy requirement by 2030 is not substantial considering India recently exported roughly 13% of the expected requirement of ~19000 GWh to neighboring countries in 2022-23.
Growing Electricity requirement with increasing EV Sales in India^
*For energy consumption calculation was done using the following assumptions: 1000km/month utilization; 2W- 4KWh battery with a range of 130km; 3W passenger- 9KWh battery with a range of 160km, 3W Goods- 9KWh battery with a range of 100km; 4W- 26KWh battery with a range of 300kms; Bus- 300KWh battery with a range of 250km
**The total energy consumption on average per vehicle is taken to be 301KWh increasing at 5% annually to factor in increasing battery efficiency. The total no. of vehicles excludes E-ricks
^The surplus is calculated without factoring in exports, imports & theft
-The electricity consumption showed a CAGR of 4.27% from 2012-13 to 2022-23, while the electricity generation and generation capacity increased at a CAGR of 5.18% and 7.7% respectively during the same period. The faster generation rate enabled India to reduce its deficit from 8.7% to 0.5% in a decade. If the trend continues, India will continue to grow at a surplus ( ~6% by 2030), despite the increasing EV energy demand as it contributes to less than 15% of the added supply.
-The AT&C losses have declined from 22% in FY 22 to 16% FY 23, showing a 27% decline. This comes in effect as Ministry of Power launched Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS) in July, 2021 to reduce the AT&C losses to pan-India levels of 12-15% and ACS-ARR (Average Cost of Supply – Average Realizable Revenue) gap to zero by 2024-25.

Conclusion
Choice between powering homes and charging EVs is not a stark binary. Grid modernization, renewable energy integration, and smart charging technologies, like off-peak charging, can harmonize electricity needs without sacrificing convenience or sustainability. This, coupled with effective theft reduction and infrastructure upgrades, paves the way for a robust future where Indian homes and EVs thrive in tandem, powered by a clean and resilient electricity grid.
Contact Us: We welcome all friends of Ev2 Ventures to reach out for an open discussion and we are just an email away for any inquiries or clarifications – Email: Team@Ev2.vc





